- April 25, 2023
- By admin_panel
- Comments 0
5G vehicle connectivity enables vehicles to connect to one another, to the infrastructure, to network services, and to other road users including bicycles and pedestrians. Therefore, making it possible for the roadways to b faster, safer, and more energyefficient.
One of the primary drivers of this shift is the emerging development of software-defined vehicles, in which a major percentage of a vehicle's operations are implemented in software that can be updated or even upgraded over time. General Motors was the first OEM to bring the first connected car capabilities to industry with OnStar (OnStar Corporation is a subsidiary of General Motors) in 1996.

V2I (Vehicle to Infrastructure): The technology records data produced by the vehicle and informs the driver about the infrastructure. The V2I technology transmits data regarding environmental, transportation, and safety conditions.
V2V (Vehicle to Vehicle): Through a wireless information exchange, the technology transmits data regarding the speed and location of nearby vehicles. The objective is to reduce traffic congestion, prevent accidents, and benefit the environment.


V2C (Vehicle to Cloud): The technology communicates with a cloud system to exchange data for and about applications used by the vehicle. This enables the vehicle to use data from other IoT-capable industries like energy, transit, and smart homes that are cloud-connected.
V2P (Vehicle to Pedestrian): The technology gathers data about its surroundings and transmits it to other vehicles, infrastructure, and individual mobile devices. This gives the vehicle a way to talk to pedestrians and is intended to improve safety and mobility on the road.

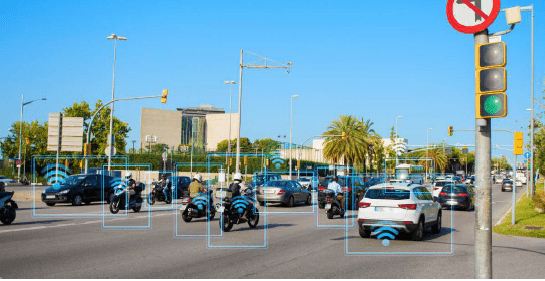
V2X (Vehicle to Everything): The technology connects all kinds of vehicles and infrastructure systems together. Cars, highways, ships, trains, and airlines all contribute to this connection.
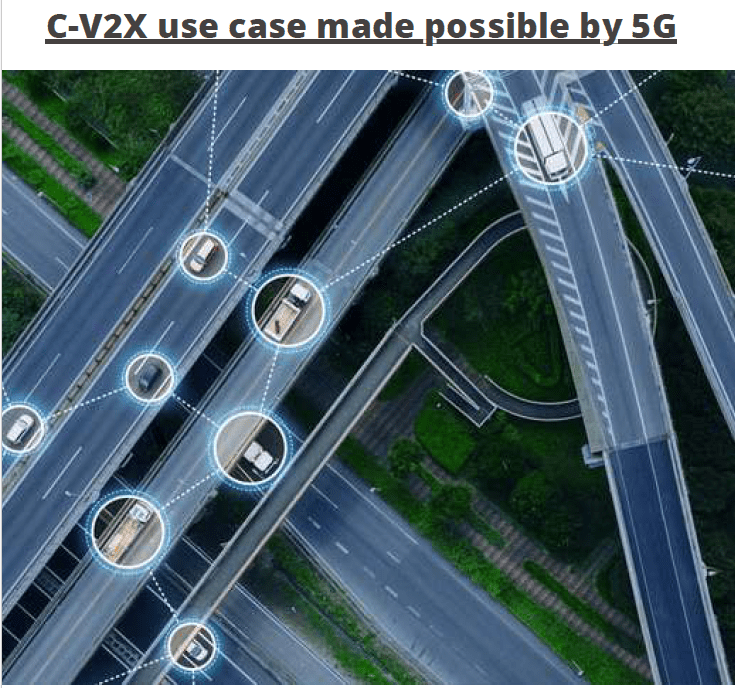
The industry standard for vehicle communication, Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (C-V2X) technology is commercially available throughout the world. This 4G and 5G-based technology, which is standardized by 3GPP, is intended to connect vehicles to one another, roadside infrastructure, pedestrians and cyclists, and cloud-based services.
Both 4G and 5G cellular networks are compatible with C-V2X. In fact, it is the only V2X technology that supports interoperability and has a roadmap to 5G while also being able to benefit from the increased bandwidth, low latency, and high reliability of next-generation networks.
In the 5G era, C-V2X will be able to support a variety of advanced safety services, such as highly accurate positioning and ranging to enable cooperative and automated driving, the delivery of local, dynamic maps based on camera and sensor data, and the extremely low latency connectivity required to support high-density platooning.
The interoperable 5G-based C-V2X connectivity groups are promoted by the 5G Automotive Association (5GAA), which categorizes vehicle applications into three groups:
Safety: C-V2X intends to minimize the frequency and severity of vehicle crashes (like warning drivers of collision risks).
Convenience: C-V2X offers diagnostics and software updates while managing data and vehicle health (like over-theair updates downloaded autonomously in safe mode and at a set time).
VRU (Vulnerable Road User): Vehicles equipped with C-V2X systems will in future be able to detect the smartphones of pedestrians and cyclists, enabling them to avoid collisions with these vulnerable road users. C-V2X facilitates safe communication between vehicles and non-vehicle road users, such as bicycles, motorcycles, and pedestrians.
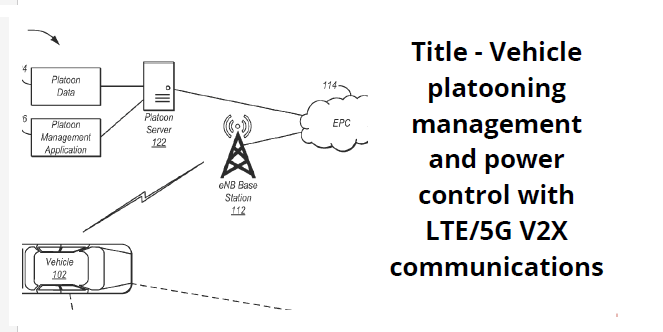
Platooning: Platooning is the formation of a vehicle movement with much closer spacing between the vehicles than can be safely achieved with human drivers. These automated movements conserve fuel, utilize road space more effectively, and increase the effectiveness of goods transportation. The transmission of information between vehicles in platoons more than three takes too long to enable synchronous braking. Consequently, platoons of more than three vehicles will also need to utilize the low latency cellular network infrastructure that will be implemented with 5G.
Co-operative driving: Cooperative driving is an advanced connected vehicle solution that allows cars to adapt to surrounding traffic. One possibility is that when one vehicle passes, the other one automatically slows down. When vehicles work together, lane changes, abrupt braking, and other
unforeseen movements are eliminated. Without 5G, cooperative driving is practically unrealistic.
Queue or Hazard Warning: C-V2X can also be used by roadside infrastructure to alert vehicles to traffic jams or construction zones so they can slow down gradually and resist hard braking.
Assistance to the emergency services: C-V2X can be utilized by police cars, ambulances, fire trucks, and other emergency vehicles to alert other traffic on their routes to clear the road so they can quickly pass through. Additionally, the C-V2X connectivity can alter traffic signals so that emergency vehicles can pass through intersections without having to slow down for moving traffic.



The first 5G private network in India was recently successfully deployed by Bharti Airtel at the Bosch Automotive Electronics India (RBAI) facility in Bengaluru. Airtel Business director & CEO Ajay Chitkara said that that the company’s 5G solution assisted Bosch shop floor managers and operators in identifying and resolving issues in real-time, thereby lowering the Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF).

SKODA AUTO has launched private 5G test network in cooperation with VODAFONE at its company’s headquarters Mladá Boleslav. SKODA AUTO has integrated the private 5G network into existing data networks in order to ensure the necessary data security and gain experience with deploying this
technology.

The Renault Group and Spanish network provider MásMóvil unveiled the R3CAV project to create 5G connected vehicles. According to MásMóvil, the R3CAV project will take on the challenge of creating a 5G vehicle communications technology that is capable of offering a driver in advance assistance in the case of complex situations.

Movandi is a US-based startup that develops 5G ecosystems for connected vehicle applications. The startup manufactures integrated antenna modules and radio-frequency (RF) chips that manage all 5G mmWave bands. This technology made it easier to adopt 5G for mobile hotspots, cellular vehicle-to-everything (CV2X), and connected vehicles.
Ettifos is a US-based startup that provides software for implementing connected mobility solutions. The startup develops a C-V2X solution using software-defined radio (SDR) that enables 5G NR sidelink-based V2X. The NR-based sidelink also promises enhancement in the form of decreased latency,
increased data rate, and support for mobility.


Freefall 5G is a US-based startup that develops a mmWave antenna system that completely utilizes 5G bandwidth while eliminating path losses. The startup’s intelligent antenna technology, known as FreeStar 5G, offers high data rate communications. The solution provides wider coverage, all-around access, & a modular design that can be adjusted to work with different frequencies & applications.
Tusk IC is a Belgian startup that conducts development and product design of IC’s for millimeter-wave spectrum applications. The start-up offers complete turnkey solutions for mmWave ICs made using the complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS), silicon on insulator (SOI), and silicon germanium (SiGe) technologies.